QR tracking at scale: simplifying maintenance without extra admin
QR tracking technology has become an essential tool for organizations seeking efficient asset management and maintenance processes. By leveraging QR codes, businesses can monitor and maintain equipment and infrastructure with minimal administrative overhead. This article explores how QR tracking at scale streamlines maintenance operations while avoiding additional paperwork, offering practical insights into its implementation and benefits.
Understanding QR tracking technology
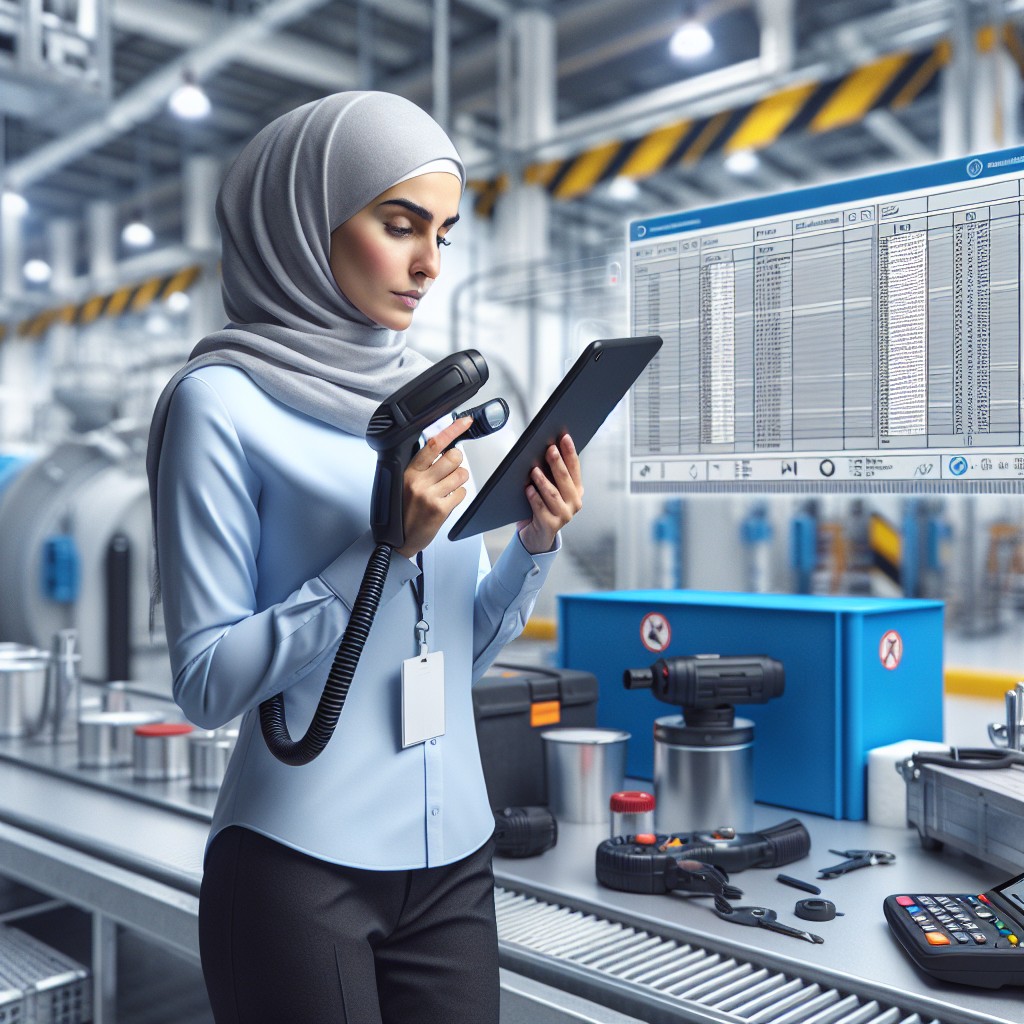
QR tracking involves using Quick Response (QR) codes to identify and monitor assets, components, or locations. When scanned, these codes direct users to digital records or databases containing detailed information about the item, such as maintenance history, specifications, and status. This technology reduces reliance on manual logs and fosters real-time updates. According to the International QR Code Committee, widespread adoption enhances data accuracy and operational efficiency. By integrating QR tracking systems, companies can reduce human errors and ensure consistent tracking across various sites and equipment.
Applications of QR tracking in maintenance management
Maintenance teams utilize QR tracking to simplify inspections, repairs, and record-keeping. Instead of filling out paper forms or entering data manually, technicians scan QR codes affixed to machinery or infrastructure components. This instantly retrieves relevant data and enables updates directly from mobile devices. Sectors like manufacturing, utilities, and transportation increasingly rely on QR tracking to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to schedule preventive maintenance. The technology supports not only internal workflows but also enhances communication between stakeholders by providing transparent access to up-to-date information.
Scaling QR tracking without increasing administrative burden
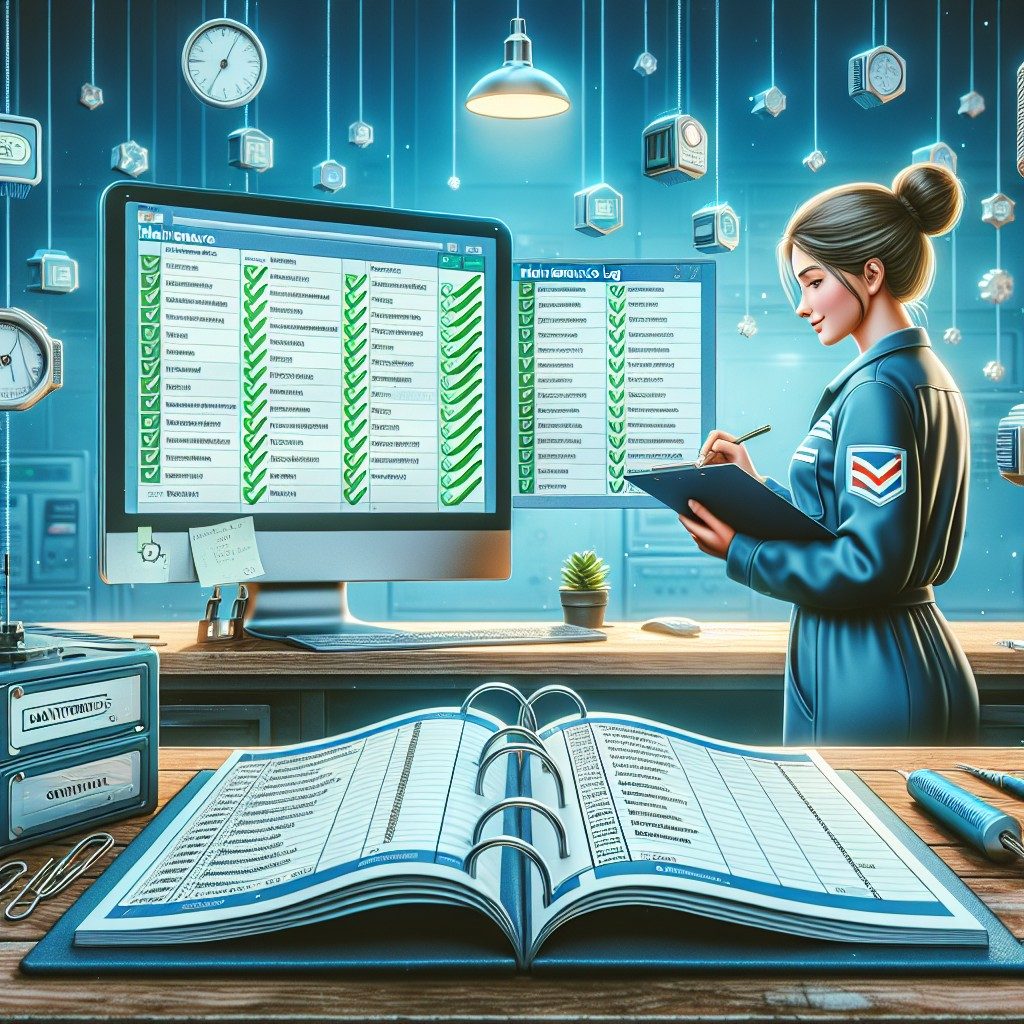
Deploying QR tracking on a large scale poses challenges, particularly in maintaining data integrity and avoiding additional administrative workload. However, modern software solutions facilitate bulk creation and management of QR codes, automate data synchronization, and integrate with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These capabilities enable organizations to scale QR tracking operations without adding complexity. Additionally, cloud-based platforms offer centralized dashboards for monitoring asset statuses and generating reports, thereby streamlining oversight and reducing manual interventions.
Benefits and performance improvements from large-scale QR tracking
The implementation of QR tracking at scale yields significant improvements in operational efficiency and maintenance quality. Real-time tracking minimizes downtime by enabling faster fault detection and resolution. The automatic documentation of maintenance activities enhances traceability and accountability. Furthermore, the use of standardized QR codes supports interoperability among diverse equipment and teams. Research published by the World Economic Forum highlights that companies leveraging QR tracking experience measurable reductions in maintenance delays and cost overruns, translating directly into improved asset longevity and compliance standards.
Challenges and best practices for successful adoption
Despite its advantages, QR tracking adoption requires careful planning to address potential issues such as data security, user training, and physical durability of QR labels. Organizations must select durable materials for QR codes to withstand environmental conditions and establish protocols to protect sensitive information accessed via QR scans. Ensuring that maintenance personnel understand the technology and its usage is crucial for maximizing effectiveness. Industry experts recommend phased rollouts and continuous evaluation to fine-tune the system and minimize disruptions during transition.
In conclusion, QR tracking at scale offers a powerful solution for simplifying maintenance processes without adding administrative complexity. Its integration into asset management frameworks fosters real-time data access, accuracy, and operational transparency. As technological capabilities evolve, the adoption of QR tracking is poised to become standard practice across sectors requiring robust maintenance regimes. Continuous innovation and adherence to best practices will drive its effectiveness, ultimately supporting sustainable and cost-efficient maintenance strategies worldwide.
For more information on the role of QR codes in industry, visiting authoritative sources such as the International Organization for Standardization can provide valuable insights and guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions about QR tracking
What is QR tracking and how does it assist in maintenance?
QR tracking is a method of using QR codes to monitor assets and maintenance activities by linking physical items to digital records, enabling quick data retrieval and updates during maintenance routines.
Can QR tracking reduce administrative tasks for maintenance teams?
Yes, by automating data collection and eliminating paper-based records, QR tracking helps maintenance teams minimize manual input, reducing administrative workload while improving accuracy.
Is QR tracking scalable for large organizations?
QR tracking systems are designed to scale efficiently through automation, integration with enterprise software, and cloud-based platforms, allowing large organizations to manage extensive asset inventories without extra administrative burden.
What challenges might arise with QR tracking implementation?
Challenges include ensuring the durability of QR codes in harsh environments, protecting data security, and providing thorough training to users for effective adoption.
Where can I find standards or guidelines related to QR tracking?
Standards and guidelines for QR tracking can be found through organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which provide frameworks for QR code usage and asset management.